Model
The core of the data package is the Ext.data.Model class. A Model or Entity
represents some object that your application manages, e.g. the (former) members
of a rock band. Models are used by stores, which are in turn used by many of the
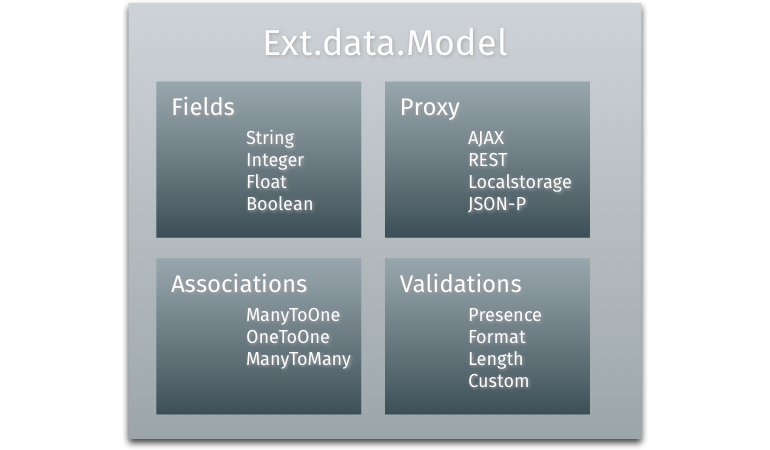
data-bound components in Ext JS. The most significant parts (or properties) of a
model are Fields (they handle the members of a model), Proxies (they handle
the loading and saving of model data), Validations (they handle validation of
the data, e.g. if a field has not-null value) and Associations (they handle the
relations and linkages to other model instances).
In this exercise we'll build up a simple model, that'll contain some (string) fields and simple validation for input data (ensuring that all fields have a value). As we only have this single model we don't want to model any associations. Please refer to the API documentation for further details. You both have the possibility to assign the proxy in the model or the store (using that model). Both ways do have advantages depending on your application setup: If you set the proxy in the model it allows you to load and save instances of this model without the need of a store and multiple stores could use the same model. In contrast defining the proxy in the store it allows you to use the same data model in multiple stores, even if the stores will load their data from different sources. In this exercise we're going to set the proxy in the store (without any specific reason).
Exercise
- (Re-)open your
index.htmland insert the following code before the instantiation of the viewport (line ~15) to create a new model calledFormerMembers:
Ext.define('FormerMembers', {
extend: 'Ext.data.Model',
fields: [{
name: 'firstName',
type: 'string'
}, {
name: 'lastName',
type: 'string'
}, {
name: 'instruments',
type: 'string'
}],
validators: {
firstName: 'presence',
lastName: 'presence',
instruments: 'presence'
}
});